4Revsピックアップ
2023年6月26日
ネットゼロによる、古代からある「不思議な素材」: バイオ炭について
#バイオ炭#未利用廃棄物#炭素削減#炭素除去技術#農業技術#農業持続可能性

概要
人口2,700万人以上のカメルーンは中央アフリカに位置する国で、2021年現在、一人当たりの二酸化炭素(CO2)排出量は0.34トン、年間排出量は930万トンである。これらの排出は、主に化石燃料の燃焼やセメント生産などの活動に起因する。CO2の大幅な排出は、天然資源への依存と、生計と糧の重要な供給源である農業部門に差し迫った課題を突きつけている。そのため、炭素除去技術をカメルーン国内だけでなく世界規模で展開することが急務となっている。
カメルーン最大のコーヒー加工工場Synergie Nord Sud (SNS)から供給され、NetZero社によって製造された廃棄コーヒー殻を原料とするバイオ炭の利用は、画期的な進歩である。バイオ炭の生産は、そのルーツをブラジルの肥沃なテラ・プレタ土壌にまで遡る、古くからある農業技術である。この黒い粉状の物質は、熱分解と呼ばれるプロセスで、酸素のない条件下(燃焼とCO2の排出を防ぐ)で、木屑、糞尿、葉、さらにはコーヒーの殻などの有機物を加熱することによって生成される。ネットゼロは、この古代の「不思議な素材」を活用して長期的な炭素除去を行う気候変動ベンチャーで、熱帯の発展途上国の農業廃棄物から炭素を抽出し、恒久的な土壌改良材(バイオ炭)と電気に変換する。2018年、気候変動に関する政府間パネルは、バイオ炭を「マイナス排出」技術として正式に指定し、地球温暖化を緩和し、気温上昇を産業革命前より1.5℃上昇に抑える上で重要な役割を認識し、破滅的な気候現象を回避する道筋を提供した。バイオ炭は、土壌肥沃度の向上、グリーンエネルギーの生成、廃棄物の削減、そして特に大気からの炭素隔離など、気候変動に対するさまざまな恩恵をもたらす。
Sustainable Development Goals Chart

メインハイライト
問題: カメルーンは現在、一人当たりの二酸化炭素排出量が0.34トンで、2021年時点の年間排出量は930万トンである。気候変動がもたらす社会経済的影響は、CO2排出にも起因しており、カメルーンの構造的貧困層と40%近い脆弱世帯の両方にダメージを与えている。非正規農業部門で働く労働者の75%近くは女性であり、気候関連の問題で最も大きな打撃を受けている。
背景:カメルーンはギニア湾に面し、中央アフリカに位置する人口2,700万人を超える国である。国土の40%以上が熱帯雨林に覆われており、800万人と推定される農村部の人々に食料、医薬品、燃料、建築資材などの伝統的な主食を供給している。
解決策: バイオ炭はマイナス排出技術であり、推定世界全体で毎年大気から除去する必要がある10ギガトンのCO2のうち、1.36~3ギガトンのCO2を取り込む能力がある。バイオ炭を活用して長期的な炭素除去を行う気候変動ベンチャーであるネットゼロ社は、熱帯の発展途上国の農業廃棄物から炭素を抽出し、恒久的な土壌改良材(バイオ炭)と電力に変換する。同社は、カメルーン西部のンコンサンバに、アフリカ初の工業規模のバイオ炭生産工場の設立に成功した。この施設では、ネットゼロは、回収した廃棄コーヒーの殻から毎年2,000トンのバイオ炭を生産し、それを小規模コーヒー農家に分配して作物を栽培させ、その農家がコーヒー加工工場に豆を供給している。炭素除去を保証するソリューションであり、世界全体で年間20億トン(CO2換算)のCO2除去が可能である。
インパクト・ステートメント:バイオ炭の生産は、農業に関連する二酸化炭素排出量を削減する上で極めて重要な役割を果たしている。バイオ炭の生産は、大気から炭素を抽出すると同時に、化学合成肥料の散布に起因する追加的な排出を抑制することで、これを達成する。この排出削減は、比例レベルを超えて、肥料の生産(CO2)と使用(N2O)の両方から排出される温室効果ガス(GHG)を含む。農地へのバイオ炭の施用は、植物の根のレベルで水と養分を効果的に保持する炭素スポンジとして機能することで土壌を強化し、土壌pHのバランスを整え、土壌の通気性を改善し、農家の作物収穫量を増加させる。
システムの視点:かつては廃棄物とみなされていたものを、炭素除去と持続可能な農業ソリューションの両方を提供する熱分解によって、マイナス排出技術に転換することは、真にユニークな革新である。農業チェーンのすべての参加者に満足と利益をもたらす循環モデルを確立するNetZeroの独特な運営アプローチは、類まれな模範であり、人類と環境の双方にとって非常に有利であることを証明している。バイオ炭は、地元で生産される製品でありながら、社会経済的な便益を伴って、世界的に大きな影響をもたらす。
事例の概要:
気候変動の世界的な影響は、人類と環境の存続を脅かし、大きな懸念材料となっている。カメルーンにおいても、気候変動は、生活と生計を天然資源と主に農業に依存している同国にとって差し迫った脅威となっている。
国土の40%以上が熱帯雨林に覆われており、800万人と推定される農村部の人々に、食料、医薬品、燃料、建築資材などの伝統的な主食を提供している。一方、気温、雨、干ばつの絶え間ない変化により、これらの人々は貧困や飢饉のリスクが高まっている。調査によると、この地域の農場全体で降水量が減ったり気温が上がったりすると、純収入が減少することが確認されている。カメルーンの農業は、季節性と水分の利用可能性による制限に頻繁に直面している。土壌の質や地形など他の物理的要因が農業に影響を与えることは間違いないが、気候が耕作作物の範囲や採用される農法の種類を形成する主な要因であることに変わりはない。2021年、農業はカメルーンのGDPに約16.91%寄与し、活動人口のほぼ70%を雇用している。
エネルギー生産、セメント生産などの産業活動、ガスのフレアリングのために化石燃料を燃やし続けているため、カメルーンは、世界銀行のアフリカ諸国のCO2排出量ランキングで30位となっている。カメルーンの国民一人当たりのCO2排出量は0.34トンで、2021年時点の年間CO2排出量は930万トンで、年々増加している。
CO2の悲惨な影響は、近年この国が経験している気候変動問題に直結している。天然資源や農業への影響もさることながら、CO2排出による気候変動問題は、幅広い社会経済的影響をもたらしている。
カメルーンの人々にとって、気候変動による社会経済的影響ショックは、カメルーンの構造的貧困層と40%近い脆弱世帯の両方に打撃を与えている。特に紛争地域や先住民族に住む女性は、非正規農業部門の労働者の75%を占め、家計の福祉と食料安全保障の主な担い手であるため、より深刻な打撃を受けている。
炭素除去ソリューション

バイオ炭は、生分解性で再生可能であれば、幅広い有機物から作られる製品である。一般的には、コーヒーやカカオの殻、サトウキビのバガス、ココナッツの殻や繊維、ピーナッツやカシューナッツの殻、パームの空房など、原料として使用される農業残渣から作られる。これらの原料は、熱分解というプロセスを経てバイオ炭になる。熱分解は、酸素のない状態で(燃焼によるCO2の排出を防ぐため)、木くず、糞尿、葉、コーヒーの殻などの有機物を加熱する。これは熱化学反応であり、複雑な分子鎖を分解して分子結合を再編成し、バイオ炭と呼ばれる固体の非常に主食性の高い生成物を形成する。
ネガティブ・エミッション技術に分類されるバイオ炭は、毎年大気中から除去される必要のある推定10ギガトンのCO2のうち、1.36ギガトンから3ギガトンのCO2を取り込む能力がある。樹木のような自然の炭素除去ソリューションが大気中のCO2削減に大きく貢献する一方で、研究によれば、それだけでは不十分である。その結果、バイオ炭は、何百年もの間、長期的かつ確実に炭素を除去できる数少ないソリューションのひとつとして際立っている。世界全体で年間20億トン(CO2換算)のCO2除去が可能なバイオ炭は、すでに利用可能な技術で大規模に導入できる最も成熟したソリューションであり、強力な科学的データに裏付けられている。
持続可能な農業のためのバイオ炭
バイオ炭は、植物の根のレベルで表土と混ぜ合わせることで、土壌改良材として農業に広く応用される。バイオ炭の使用は、植物が光合成の際に空気中から取り込んだ炭素を、不活性な固体の形で土壌に貯蔵することを意味する。このバイオ炭の一回の施用は、農家にとってコストと負債を増大させる肥料を毎年施用しなければならないのとは対照的に、長期にわたる農学的利益をもたらす。バイオ炭の物理化学的特性は、いくつかの点で土壌の品質向上に寄与している。
第一に、バイオ炭の優れた多孔性は、土壌の保水力を高め、植物に十分な水分を供給する。スポンジのように、バイオ炭は多くの細孔を持ち、炭素を多く含む物質に驚くほど高い表面積を与える。1グラムのバイオ炭の表面積はサッカー場1面分にもなります。バイオ炭は土壌に栄養分を与えるわけではありませんが、バイオ炭の表面はマイナスに帯電しているため、必要な栄養分が保持されやすく、植物が効率よく栄養分を取り込むことができます。さらに、バイオ炭の高い炭素含有量は酸性土壌のバランスを整え、植物の健全な成長のためにpHレベルを最適化する。これらの要素を総合すると、作物の生産性が持続的に向上し、100%有機農法への移行が可能になります。研究によると、熱帯土壌では、高栄養バイオ炭の投入は低栄養バイオ炭よりも収量を大幅に刺激し、生産性は平均25%向上した。しかし、温帯土壌ではバイオ炭の投入は作物収量に何の効果も示さないことに注意することが重要である。

バイオ炭、肥料、コントロールのトウモロコシ圃場試験。写真出典:NetZero
NetZero:再現可能なモデル
アクセル・レイノー、オリヴィエ・レイノー、ペドロ・デ・フィゲイレド、エイム・ンジャキンによって2021年に設立されたフランスのスタートアップ企業NetZero は、大気からの長期的な炭素除去のための数少ない実行可能なソリューションであるバイオ炭の採用を拡大するという明確な使命を持っている。熱帯地域で事業を展開し、バイオ炭の多様なコベネフィットを活用することで、ネットゼロの革新的なアプローチは、発展途上国における気候変動、持続可能な農業、農村開発という3つの重要な課題に同時に取り組んでいる。
ネットゼロは、カメルーン西部のンクンサンバに、アフリカ初の工業規模のバイオ炭製造プラントを設立した。ンクンサンバとその周辺は、カメルーン最大のコーヒー農園として知られている。カメルーン最大のコーヒー加工工場であるシナジー・ノール・スッド(SNS)から排出されるコーヒーの籾殻を利用することで、これらのバイオマス原料は埋立地でゆっくりと腐敗するのを放置されることはない。その代わりに、ネットゼロの施設に運ばれ、そこで変質プロセスを経て、気候変動の緩和において重要な役割を果たす可能性を秘めた驚くべき素材に生まれ変わる。NetZeroは、地元で入手可能な未利用作物残渣の豊富な利用可能性を活用し、この地域循環モデルを他の熱帯途上国でも再現することを目指している。
ンコンサンバにあるネットゼロの最初のパイロット・プラントは、毎年最大2,000トンのバイオ炭を生産している。この製品は小規模コーヒー農家に配布され、土壌の肥沃度を向上させ、作物を栽培するのに役立っている。
バイオ炭の製造プロセスは多くの利点をもたらす一方で、特に熱エネルギーの消費が大きいという点で、一定の制限もある。熱分解の際にバイオマスを加熱すると、メタンや水素などの可燃性ガスが発生する可能性がある。しかし、ネットゼロはこの課題に効果的に対処するモデルを考案した。これらのガスの一部をオーブンの燃料に転換して必要な熱を供給し、残りのガスは再生可能な電力に転換して周辺地域に配給する。この戦略的アプローチにより、ネットゼロは副生ガスを事業内で効率的に管理・利用することができる。
ネットゼロの中核的な目標のひとつは、2030年までに毎年200万トンのCO2を大気から除去できるように、ンコンサンバのモデルを大規模に再現することである。2021年のCOP26で、同社は主要パートナーシップをカメルーン政府と締結し、2030年までに同国に少なくとも50カ所のバイオ炭生産サイトを建設し、毎年少なくとも25万トンのCO2を大気から除去できるようにする。同社は、ミミズ基金と協力し、合成肥料の代わりにバイオ炭を使用することの共同利益について、農家への現場研修と教育を実施している。
2023年4月、ネットゼロはブラジルに年産5,000トンの施設を開設し、作物残渣を利用したバイオ炭施設としては世界最大となる。これは、6,500トン以上の大気中のCO2に相当する量を除去すると同時に、農業に耐久性のある肥料化ソリューションをもたらすことになる。2023年末までに、ネットゼロはブラジルに2つの生産工場を建設し、バイオ炭を大規模に生産する独自のモデルを活用する予定である。
ネットゼロは、イーロン・マスクのXPRIZE炭素除去コンペティションのマイルストーン賞、ソーラー・インパルス財団の「効率的ソリューション」ラベル、テック・フォー・グッド・アワードのグリーンテック賞、ピューロ・スタンダードの認定炭素除去プロジェクトなど、特に優れた評価を得ている。Puro.earth手法の要件への適合は、独立した評価者によって行われる。審査員は生産施設を訪問し、ライフサイクルアセスメント(LCA)または環境製品宣言(EPD)報告書に記載されたカーボン・ネット・マイナスの証拠を含むデータの正確性を検証し、審査報告書を発行します。ピューロ・スタンダードは、ネットゼロに付与されたバイオベースのカーボン・クレジットを認証し、そのカーボン・クレジットは、排出量の相殺を求める企業によって購入される。これは、企業や投資家が効果的な炭素除去ソリューションに資源を振り向ける可能性を提供すると同時に、ネットゼロがバイオ炭設備の規模を拡大し、他の熱帯地域に事業を拡大することを可能にする。

ブラジル、ラジーニャにあるネットゼロ社のバイオ炭プラント。写真出典:NetZero

ブラジルのラジーニャのバイオ炭プラント。
カメルーンでバイオ炭を作物に散布する農家。写真出典:Earthworm Foundation
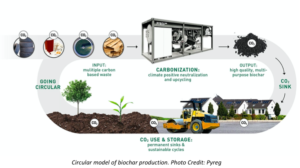
バイオ炭の循環モデル。
バイオ炭製造の円形モデル。写真出典:Pyreg
インパクト・ステートメント
カメルーンでの試験的生産施設を通じて、ネットゼロの成功は、炭素除去と持続可能な農業の両方において、体系的な影響を拡大する大きな機会を生み出した。
炭素除去のプロセスにおいて、バイオ炭はその主な化学成分である炭素によって効果的な解決策となる。この炭素は大気から発生し、光合成の過程で植物に取り込まれる。熱分解の過程でバイオ炭が土壌に取り込まれると、この炭素が抽出され安定化する。重要なことは、一度土壌に取り込まれた炭素は、数百年という長期にわたって隔離され続けるということである。要するに、バイオ炭は環境から炭素を除去する長期的かつ永続的な手段として登場したのである。
炭素除去に加え、ネットゼロのエンド・ツー・エンド・オペレーション・モデルは、環境と社会への影響を最大化する。
・合成肥料の使用を減らすことで、肥料の生産(CO2)と使用(N2O)から排出される温室効果ガスを比例して削減する。
・農村部において、有能で給与の高い産業雇用を創出する。
・バイオ炭の販売価格を補助し、農家が購入しやすい価格にする。
・バイオ炭を使って収量を向上させ、農家の収入を増やす。
・24時間365日安定した再生可能な電力を地域で利用する。
ネットゼロのバイオ炭は、さまざまなメリットを提供することで、持続可能な農業の促進に極めて重要な役割を果たしている。バイオ炭を農地に散布することで、炭素スポンジとして土壌を強化し、植物の根レベルで水と養分を効果的に保持し、土壌pHのバランスを整え、土壌の通気性を改善し、農家の収穫量を増加させる。
取引の観点からは、ネットゼロのバイオ炭の利用は、加工作物の買い手、協同組合、加工施設に大きなメリットをもたらす。より高品質の製品を仕入れることができ、同時に二酸化炭素排出量も削減できる。
さらに、バイオ炭は化学合成肥料への依存を減らし、100%有機栽培への転換の可能性を示している。この転換は、環境の持続可能性を向上させるだけでなく、農業のカーボンフットプリントの削減にも貢献する。大気中の炭素を除去し、肥料の生産と使用に伴う排出を抑制することで、バイオ炭は気候変動の影響を緩和する上で重要な役割を果たしている。
イーロン・マスクのXPRIZE炭素除去コンペティションでマイルストーン賞を受賞したネットゼロのアプローチは、農業チェーンにおけるさまざまなステークホルダーに利益をもたらす、循環型のWin-Winモデルとして評価されている。このバイオ炭の包括的な利用は、関係者すべてにとって持続可能で互恵的なシステムを育む。
カーボン・マイナス排出と農業生産性の向上を実現するネットゼロのモデルは、国連の持続可能な開発目標(Sustainable Development Goals)の実現に貢献する絶好の機会である:
#1:貧困ゼロ(調達とパートナーシップを通じて、農村部の持続可能な生活を支援する)
#2:飢餓ゼロ(土壌の肥沃度と作物の収穫量を向上させることで、バイオ炭は食料安全保障の強化に貢献し、飢餓ゼロを達成する努力を支援する)
#7位:安価でクリーンなエネルギー(ネットゼロがバイオ炭の生産を利用し、熱と発電のためにガスを転換することは、クリーンで安価なエネルギーへのアクセスを促進するという目標に合致している)
#8:ディーセント・ワークと経済成長(特にバイオ炭の生産と農業への恩恵が実現する農村部での雇用機会の創出)
#9:産業、技術革新、インフラストラクチャー(バイオ炭製造に対するネットゼロの革新的なアプローチと産業規模の施設の設立は、産業、技術革新、インフラストラクチャーの発展に貢献する)
#12位:責任ある消費と生産(ネットゼロの循環型モデルと廃棄コーヒー殻の原料利用は、責任ある消費と生産という目標に合致しており、廃棄物を削減し、資源を効率的に利用する)
#13位:気候変動対策(大気中の炭素を除去し、温室効果ガスの排出を削減し、気候変動を緩和するマイナス・エミッション技術を提供する)
#15位:土地の生命(土壌の質を高め、持続可能な農業を促進し、荒廃した土地の回復を支援することで、生物多様性の保全と土地の生態系の健全性を支える)。
システムの視点
バイオ炭は、炭素除去や持続可能な農業への潜在的な応用や利点が近年になって注目され、認識されるようになったため、現代の気候変動緩和の取り組みにおいて「新しい」技術と呼ばれることが多い。バイオ炭の製造方法自体は数千年前に遡る古いものであるが、現代の科学的研究、技術的進歩、そして大規模な実施への統合は比較的新しいものである。
バイオ炭の歴史的な利用は、炭化バイオマスの施用によって肥沃なテラ・プレタ土壌を作り出したアマゾン人のような古代文明にまで遡ることができる。しかし、バイオ炭の特性、製造技術、炭素貯留の可能性について、より広く認識され、科学的に理解されるようになったのは最近のことである。
バイオ炭に対する最近の関心は、気候変動を緩和し、持続可能な農業の解決策を見出すという緊急の必要性からきている。研究者や専門家は、バイオ炭が炭素を隔離し、土壌の肥沃度を高め、保水性を向上させ、温室効果ガスの排出を削減する能力を持つことを認識している。これらの特性と大規模な導入の可能性を併せ持つバイオ炭は、気候変動と持続可能な農業の両方に取り組むための有望なツールである。
さらに、技術と科学的理解の進歩により、バイオ炭の特性と潜在的な用途をより深く探求することが可能になった。最新の熱分解技術、土壌力学の理解、先進的なモデリングと測定ツールの統合は、炭素除去のための貴重で効果的な技術としてバイオ炭に再び関心を持たせることに貢献している。
バイオ炭の効果を最大限に発揮させるためには、土壌の種類や条件に合わせて適用することが重要である。温帯気候の土壌の場合、有機物の含有量が多い土壌や化学的性質の異なる土壌では、バイオ炭の効果が限定的な場合もある。バイオ炭の生産には、バイオマス原料の安定供給も必要である。農業残渣や廃棄物のようなバイオマス原料の入手可能性と持続可能性は、地域や時間によって異なり、特定の地域で事業を拡大する際の課題となり得る。
また、バイオ炭の生産には高い熱エネルギーが必要であり、熱分解の過程で温室効果ガスが排出される可能性がある。バイオ炭製造のエネルギー集約的な性質は、排出を最小限に抑え、正味のカーボン・マイナス・プロセスを確実にするために注意深く管理されるべきである。
ネットゼロのバイオ炭製造における熱分解プロセスの活用は、バイオ炭が何百年もの間、土壌に残留することを可能にする耐久性を示唆している。しかし、バイオ炭は長期間にわたって土壌に炭素を隔離する能力を持つが、その炭素隔離の可能性は土壌の種類、気候条件、管理方法などの要因によって異なる可能性がある。実際に隔離される炭素の量は、これらの変数によって影響を受ける可能性がある。土壌の健全性、栄養循環、微生物活性に対するバイオ炭の長期的な指標については、さらなる研究が必要である。
バイオ炭は主に地域レベルで利用されているが、世界的な影響を与えることができ、社会経済的に大きなメリットを生む。カメルーンのように、気候変動によって社会経済的な課題に直面している国では、ネットゼロのバイオ炭生産は、環境、経済、社会の各領域における安定、成長、回復力のためのタイムリーな解決策となる。
カメルーン、ブラジル、その他の熱帯諸国でバイオ炭生産の規模を拡大し、より大量に生産するというネットゼロの目標は、称賛に値する前進である。世界のステークホルダーは、これを環境と未来に投資し、持続可能で繁栄する地球に貢献するまたとない機会として認識すべきである。
関連リンク
ネットゼロのウェブサイト https://netzero.green/en/biochar/
***
人類は、地球上の生命が繁栄し続けるために克服しなければならない4つの必須生存課題(4Revs)、すなわちボトルネックに直面している: 食料、水、資源、気候変動/エネルギーである(詳細は後述)。これら4つの分野は、革命的なイノベーションを必要とすると同時に、新たなチャンスの宝庫でもある。
4Revsは、人類がこれら4つの分野を解決できるよう支援することを目的とした、ユニークで共創的なエコシステムです。
4Revsは、2020年から2050年の間に、人類が1世代でこれら4つの生存の課題を解決することを目指す、ユニークな共創エコシステムです。
Jun 26, 2023
NetZero’s Ancient ‘Wonder Material’: Biochar
#biochar#waste-product#carbon-reduction#carbon-removal-technology#agro-technology#agricultural-sustainability
Abstract
With a population of more than 27 million people, Cameroon is a country in Central Africa with a carbon dioxide (CO2) emission per capita of 0.34 metric tons and annual emission of 9.30 million tons as of 2021. These emissions primarily stem from activities such as fossil fuel combustion and cement production. The significant release of CO2 poses a pressing challenge to the nation’s reliance on natural resources and its agricultural sector, which serves as a vital source of livelihood and sustenance. Consequently, there exists an urgent imperative to deploy carbon removal technologies at scale within Cameroon and worldwide.
The utilization of biochar, derived from waste coffee husks sourced from Synergie Nord Sud (SNS), the largest coffee-processing plant in Cameroon, and produced by NetZero, has emerged as a remarkable breakthrough. Biochar production is an age-old agricultural technique that traces its roots back thousands of years to the fertile Terra Preta soils of Brazil. This black powdery substance is generated through the heating of organic materials like wood chips, manure, leaves, and even coffee husks, under oxygen-free conditions (preventing combustion and CO2 emissions) in a process called pyrolysis. NetZero, a climate venture leveraging this ancient “wonder material” to perform long-term carbon removal, extracts carbon from agricultural waste in tropical developing countries, and converts it into a permanent soil amendment (biochar) and electricity. In 2018, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change officially designated biochar as a “negative emissions” technology, recognizing its crucial role in mitigating global warming and limiting temperature rise to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, thus offering a pathway to avert catastrophic climate events. With its array of climate benefits such as enhanced soil fertility, generation of green energy, waste reduction, and notably, carbon sequestration from the atmosphere, biochar has the potential to sequester a significant portion of the approximately 10 gigatons of CO2 globally that requires extraction from the atmosphere annually, with estimates ranging from 1.36 to 3 gigatons.
Sustainable Development Goals Chart

Main Highlights
The Problem: Cameroon currently exhibits a per capita carbon dioxide emission of 0.34 metric tons and an annual emission of 9.30 million tons as of 2021. The socioeconomic impact of climate change, which is also driven by CO2 emissions, is damaging both the structural poor and the close to 40% of vulnerable households in Cameroon. Nearly 75% of the workers in the informal agricultural sector are women and are worst hit by climate-related issues.
The Context: Cameroon is a country found on the Gulf of Guinea and located in Central Africa with a population exceeding 27 million people. Over 40% of the country is covered by tropical forests and this provides an estimated 8 million rural people with traditional staples including food, medicines, fuel, and construction materials.
The Solution: Biochar is a negative emission technology, with the capacity to take up 1.36 to 3 gigatons of CO2 out of the estimated 10 gigatons of CO2 that is needed to be removed from the atmosphere each year globally. NetZero, a climate venture leveraging biochar to perform long-term carbon removal, extracts carbon from agricultural waste in tropical developing countries, and converts it into a permanent soil amendment (biochar) and electricity. The company has successfully established Africa’s first industrial-scale biochar production plant located in Nkongsamba in western Cameroon. In this facility, NetZero produces 2,000 tons of biochar each year from waste coffee husks collected, which is then distributed to small scale coffee farmers to cultivate crops, who in turn supply the coffee processing factory with beans. It is a guaranteed carbon removal solution with a global sustainable removal capacity of up to 2 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent a year.
Impact Statement: The production of biochar plays a pivotal role in diminishing the carbon footprint associated with agriculture. It achieves this by simultaneously extracting carbon from the atmosphere and curbing additional emissions stemming from the application of synthetic fertilizers. This reduction in emissions extends beyond proportionate levels, encompassing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from both fertilizer production (CO2) and usage (N2O). The application of biochar on agricultural land enhances the soil by acting as a carbon sponge that effectively retains water and nutrients at plant root level, rebalances soil pH, improves soil aeration and increases crop yield for farmers.
System Perspective: The conversion of what was once considered waste into a negative emissions technology through pyrolysis, offering both carbon removal and sustainable agricultural solutions, represents a truly unique innovation. NetZero’s distinctive operational approach, establishing a circular model that ensures satisfaction and benefits all participants in the agricultural chain, sets an exceptional example and proves highly advantageous for both humanity and the environment. Biochar, a locally produced product, yields significant global impacts, accompanied by substantial socioeconomic benefits.
Case Overview
The global impact of climate change has become a huge cause for concern as it threatens the existence of humans and the environment. In Cameroon, climate change is also an imminent threat to the country’s dependence on natural resources and mostly agriculture for livelihoods and subsistence.
Over 40% of the country is covered by tropical forests, which provides an estimated 8 million rural people with traditional staples including food, medicines, fuel and construction materials. Meanwhile, constant changes in temperature, rain, and droughts are putting these populations at greater risks for increased poverty and famine. Research confirms that net revenues decline when precipitation decreases or temperatures rise across farms in the region. Agriculture in Cameroon frequently faces limitations imposed by seasonality and the availability of moisture. While other physical factors like soil quality and topography undoubtedly influence agriculture, climate remains the predominant factor shaping the range of cultivated crops and the types of agricultural practices employed. In 2021, agriculture contributed around 16.91% to the GDP of Cameroon, and employs nearly 70% of the active population.
With the continued burning of fossil fuel for energy production, industrial activities such as cement production and gas flaring, Cameroon has ranked 30th in the World Bank ranking of African countries on CO2 emissions. Cameroon’s CO2 emission per capita stands at 0.34 metric tons, and the country’s annual CO2 emission stands at 9.30 million tons as of 2021, increasing year on year.
The disastrous impact of CO2 is directly related to the climate change issues experienced by the country in recent years. Asides its effect on natural resources and agriculture, the climate change issues also driven by CO2 emission has resulted in wide-ranging socioeconomic impacts.
For Cameroonians, the socioeconomic impact of climate change shocks is hurting both the structural poor and the close to 40% of vulnerable households in Cameroon. Women, especially those living in conflict areas or indigenous groups, are more severely hit, as they account for 75% of the workers in the informal agricultural sector and are primarily responsible for the welfare of their households and food security.
A Carbon Removal Solution

Biochar is a product made from a wide range of organic matter, provided it is biodegradable and renewable. It is commonly made from agricultural residues used as a feedstock, such as coffee or cocoa husks and shells; sugarcane bagasse; coconut shells and fibers; peanut or cashew shells; and palm empty bunches. These feedstocks are turned into biochar through pyrolysis, a process involving heating up organic matter such as wood chips, manure, leaves, or coffee husks, in the absence of oxygen (in order to prevent combustion, which would emit CO2). It is a thermochemical reaction that breaks down complex molecular chains and rearranges molecular bonds to form a solid, very staple product called biochar.
Classified as a negative emission technology, biochar has the capacity to take up 1.36 to 3 gigatons of CO2 out of the estimated 10 gigatons of CO2 that is needed to be removed from the atmosphere each year. While natural carbon removal solutions like trees contribute substantially to CO2 reduction in the atmosphere, research indicates that they alone will not be sufficient. Consequently, biochar stands out as one of the few solutions capable of providing prolonged and assured carbon removal for hundreds of years. With a global sustainable removal capacity of up to 2 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent annually, biochar offers the most mature solution to be brought at scale with already available technology and supported by strong science-based data.
Biochar for Sustainable Agriculture
Biochar finds extensive application in agriculture as a soil amendment, precisely when mixed with topsoil at the plant root level. Using biochar means storing carbon, captured from the air by plants during photosynthesis, in the soil in an inert solid form. This single application of biochar yields long-lasting agronomic benefits, in contrast to fertilizer which has to be applied annually, raising costs and debt for farmers. The physicochemical characteristics of biochar contribute to enhancing soil quality in several ways.
Firstly, its remarkable porosity significantly improves the water-holding capacity of soils, ensuring adequate moisture availability for plants. Like a sponge, biochar contains many pores that give the carbon-rich material an amazingly high surface area. One gram of biochar can have a surface area of a football field. While biochar does not introduce nutrients to the soil, the negatively charged surface of biochar enables better retention of essential nutrients, promoting their efficient uptake by plants. Furthermore, the high carbon content of biochar aids in rebalancing acidic soils, optimizing pH levels for healthy plant growth. Collectively, these factors culminate in a sustainable enhancement of crop productivity, enabling the potential transition to 100% organic farming practices. Research shows, in tropical soils, high-nutrient biochar inputs stimulated yield substantially more than low-nutrient biochar, where productivity is raised by 25% on average. However, it is important to note, in temperate soils, the application of biochar has no demonstrated effect on crop yield.

Maize field trials with biochar, fertilizer, and control. Photo Credit: NetZero
NetZero: A Replicable Model
Founded in 2021 by Axel Reinaud, Olivier Reinaud, Pedro de Figueiredo and Aime Njiakin, the French start-up NetZero has a clear mission to scale up the adoption of biochar, one of the few viable solutions for long-term carbon removal from the atmosphere. By operating in tropical regions and capitalizing on the diverse co-benefits of biochar, NetZero’s innovative approach simultaneously addresses three critical challenges in developing nations: climate change, sustainable agriculture, and rural development.
NetZero has successfully established Africa’s first industrial-scale biochar production plant located in Nkongsamba in western Cameroon. Nkongsamba and its surroundings are best known for the country’s largest coffee farms. By harnessing the waste coffee husks produced by Synergie Nord Sud (SNS), the largest coffee-processing plant in Cameroon, these biomass materials are not left to slowly decay in landfills. Instead, they are transported to the NetZero facility where they undergo a transformative process, turning them into a remarkable material with the potential to play a crucial role in climate change mitigation. NetZero aims to replicate this local and circular model in other tropical developing countries, leveraging the abundant availability of locally accessible unused crop residues.
NetZero’s first pilot plant in Nkongsamba produces up to 2,000 tons of biochar each year. These products are distributed to small scale coffee farmers to help improve soil fertility and cultivate crops, who in turn supply SNS’s coffee processing factory with beans.
While the biochar production process brings numerous benefits, it also comes with certain limitations, particularly in terms of high thermal energy consumption. The heating of biomass during pyrolysis can generate flammable gasses, including methane and hydrogen. However, NetZero has devised a model that effectively addresses this challenge. A portion of these gasses is redirected to fuel the oven, thereby providing the necessary heat, while the remaining gasses are converted into renewable electricity distributed to surrounding communities. This strategic approach enables NetZero to manage and utilize the byproduct gasses efficiently within their operations.
One of the core objectives of NetZero is to replicate the model from Nkongsamba on a large scale in order to be able to remove 2 million tons of CO2 from the atmosphere each year by 2030. At COP26 in 2021, the company launched a major partnership with the Government of Cameroon to construct at least 50 biochar production sites in the country before 2030, allowing to remove from the atmosphere at least 250,000 tonnes of CO2 every year. The company is working with the Earthworm Foundation to deliver field training and education to farmers about the co-benefits of using biochar in place of synthetic fertilizers.
In April of 2023, NetZero opened a facility in Brazil with a capacity of 5,000 tons per year, making it the largest biochar facility in the world using crop residues. This will remove the equivalent of more than 6,500 tons of atmospheric CO2, while bringing a durable fertilization solution for agriculture. Before the end of 2023, NetZero will build two other production plants in Brazil, leveraging its unique model to bring biochar at scale.
NetZero has achieved exceptional recognition, most notably: the Milestone Award in Elon Musk’s XPRIZE Carbon Removal competition, the ‘Efficient Solution’ label by the Solar Impulse Foundation, the Green Tech prize from Tech for Good Awards, and a certified carbon-removal project under the Puro Standard. Compliance to Puro.earth methodology requirements is done by an independent assessor. Their auditor visits the production facility, validates the accuracy of data, including the carbon net-negativity evidence presented in a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) or Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) report, and issues an audit statement. The Puro Standards certifies bio-based carbon credits awarded to NetZero, which are then purchased by companies seeking to offset their emissions. This offers potential for businesses and investors to channel resources towards effective carbon removal solutions, while also enabling NetZero to scale up its biochar facilities and expand its operations into other tropical regions.

NetZero biochar plant in Lajinha, Brazil. Photo Credit: NetZero

Farmers applying biochar to crops in Cameroon. Photo Credit: Earthworm Foundation

Circular model of biochar production. Photo Credit: Pyreg
Impact Statement
Through its pilot production facility in Cameroon, NetZero’s success has created a huge opportunity to scale systemic impact in both carbon removal and sustainable agriculture.
In the process of carbon removal, biochar serves as an effective solution primarily due to its main chemical component: carbon. This carbon originates from the atmosphere, captured by plants through the process of photosynthesis. During the pyrolysis process, when biochar is incorporated into the soil, this carbon is extracted and stabilized. Importantly, once in the soil, the carbon remains sequestered for extended periods, spanning hundreds of years. In essence, biochar emerges as a long-term and enduring means of removing carbon from the environment.
In addition to carbon removal, NetZero’s end-to-end operations model maximizes environmental and social impact by:
● Reducing the application of synthetic fertilizers which reduces more than proportionately GHG emissions from fertilizer production (CO2) and use (N2O)
● Creating qualified, well paid industrial jobs in rural areas
● Subsidizing the selling price of biochar for farmers, making it affordable
● Increasing the income for farmers by using the biochar to improve yields
● Generating 24/7 stable and renewable electricity for local use.
NetZero’s biochar plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainable agriculture by offering a range of benefits. The application of biochar on agricultural land enhances the soil by acting as a carbon sponge that effectively retains water and nutrients at plant root level, rebalances soil pH, improves soil aeration and increases crop yield for farmers.
From a trading perspective, the utilization of NetZero’s biochar provides significant advantages to buyers of processed crops, cooperatives, and processing facilities. They can source higher-quality products while simultaneously reducing their carbon footprint.
Moreover, biochar aids in reducing the reliance on synthetic fertilizers, presenting the potential for a transition towards 100% organic production. This shift not only helps improve environmental sustainability but also contributes to reducing the carbon footprint of agriculture. By removing carbon from the atmosphere and curbing emissions associated with fertilizer production and use, biochar plays a critical role in mitigating climate change impacts.
As a recipient of the Milestone Award in Elon Musk’s XPRIZE Carbon Removal competition, NetZero’s approach is recognized for its circular win-win model, wherein the benefits extend to various stakeholders in the agricultural chain. This comprehensive utilization of biochar fosters a sustainable and mutually beneficial system for all involved.
NetZero’s model for carbon negative emissions and increased agricultural productivity presents an enormous opportunity to help realize the UN Sustainable Development Goals, namely:
#1: No Poverty (by supporting sustainable livelihoods in rural areas through procurement and partnerships)
#2: Zero Hunger (by improving soil fertility and crop yield, biochar helps to enhance food security and supports efforts to achieve zero hunger)
#7: Affordable and Clean Energy (NetZero’s utilization of biochar production by redirecting gasses for heat and electricity generation aligns with the goal of promoting clean and affordable energy access)
#8: Decent Work and Economic Growth (by creating job opportunities, particularly in rural areas, where biochar production and agricultural benefits are realized)
#9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure (NetZero’s innovative approach to biochar production and its establishment of industrial-scale facilities contribute to advancing industry, innovation, and infrastructure)
#12: Responsible Consumption and Production (NetZero’s circular model and use of waste coffee husks as feedstock align with the goal of responsible consumption and production, reducing waste and utilizing resources efficiently)
#13: Climate Action (providing a negative emission technology that helps remove carbon from the atmosphere, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change)
#15: Life on Land (enhances soil quality, promotes sustainable agriculture, and helps restore degraded land, supporting biodiversity conservation and land ecosystem health).
Systems Perspective
Biochar is often referred to as a “new” technology in the context of modern climate change mitigation efforts because its potential applications and benefits for carbon removal and sustainable agriculture have gained significant attention and recognition only in recent years. While the practice of making biochar itself is indeed ancient, dating back thousands of years, its integration into contemporary scientific research, technological advancements, and large-scale implementation is relatively new.
The historical use of biochar can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Amazonians, who created fertile Terra Preta soils through the application of charred biomass. However, the broader awareness and scientific understanding of biochar’s properties, production techniques, and potential for carbon sequestration have emerged more recently.
The modern interest in biochar as a technology stems from the urgent need to mitigate climate change and find sustainable solutions for agricultural practices. Researchers and experts have recognized biochar’s ability to sequester carbon, enhance soil fertility, improve water retention, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These characteristics, combined with its potential for large-scale implementation, make biochar a promising tool for addressing both climate change and sustainable agriculture.
Furthermore, advancements in technology and scientific understanding have enabled a deeper exploration of biochar’s properties and potential applications. With the capacity to offset 12% of global greenhouse gas emissions and offering numerous co-benefits, the integration of modern pyrolysis techniques, improved understanding of soil dynamics, and advanced modeling and measurement tools have contributed to the renewed interest in biochar as a valuable and effective technology for carbon removal.
It is important to note biochar application should be tailored to specific soil types and conditions to maximize its benefits. In certain cases –within temperate climates as highlighted in the case overview– biochar application may have limited effects on soils with already high organic matter content or specific chemical properties. Biochar production also requires a steady supply of biomass feedstock. The availability and sustainability of biomass sources, such as agricultural residues or waste products, may vary regionally and over time and can pose a challenge to scaling up operations in certain areas..
Another caveat is that the production of biochar involves high thermal energy utilization, which can result in the release of greenhouse gas emissions during the pyrolysis process. The energy-intensive nature of biochar production should be carefully managed to minimize emissions and ensure a net carbon-negative process.
NetZero’s utilization of the pyrolysis process in biochar production suggests its durability, allowing it to remain in the soil for hundreds of years. However, while biochar has the capacity to sequester carbon in the soil for extended periods, its carbon sequestration potential may vary depending on factors such as soil type, climate conditions, and management practices. The actual amount of carbon sequestered can be influenced by these variables. The long-term metrics of biochar on soil health, nutrient cycling, and microbial activity require further research.
Although predominantly used at a local level, biochar can have a global impact, generating substantial socioeconomic advantages. In countries like Cameroon, where rural communities face socioeconomic challenges exacerbated by climate change, NetZero’s biochar production provides a timely solution for stability, growth and resilience across environmental, economic and social domains.
NetZero’s objective to scale up biochar production in Cameroon, Brazil, and other tropical countries, and produce larger quantities represents a commendable step forward. Global stakeholders should recognize it as a unique opportunity to invest in the environment and the future, contributing to a sustainable and thriving planet.
Links
NetZero Website: https://netzero.green/en/biochar/
***
Humanity is facing four essential survival challenges (4Revs) – or bottlenecks – which we must overcome to enable the continued flourishing of life on Earth: Food, water, resources, and climate change/energy (details below). These four areas will require revolutionary innovation and, at the same time, provide a treasure trove of new opportunities.
4Revs is a unique, co-creative ecosystem
that aims to help humanity solve these four survival challenges in one generation – between 2020-2050.
Thank you for partnering with us.
Contact
https://4revs.net/contact/
最新のピックアップ
-
2024年3月8日
Mar 8, 2024
lithium battery; energy transition; recycling; closed loop

-
2024年3月6日
Mar 6, 2024
Tomato Jos: Investment & Impact into Nigeria’s Tomato Industry

-
2024年3月4日
Mar 4, 2024
ネイチャー・ポジティブに資する 投資は、世界全体のわずか 3%に過ぎない
Only 3 per cent of global investments are nature- positive

-
2024年2月3日
Feb 3, 2024
Towards sustainable regenerative food systems

-
2024年1月4日
Jan 4, 2024
Climate adaptation – 150 options for water in agriculture

